How to configure VPN in Windows 10
This article defines Virtual Private Network (VPN) and the three basic connection types of VPN: remote user, third-party to mask source IP and user activities, and site-to-site-VPN. It also illustrates how remote user VPN is established using in-built Windows 10 VPN client.
This article is designed for professionals and self-starters who want to understand from basics to the setup and requirements for VPN. We’ll also give a practical description of how to use Windows 10 to connect to a Mikrotik VPN server.
Learn Windows 10 Host Security
What is a Virtual Private Network (VPN)?
A VPN is a private network that uses a public network (usually the internet) to connect remote sites or users together.
Even though VPN was initially used to establish secure remote connections to an organization’s network, it’s now being used by users to conceal their online activities and geographic location. It sometimes poses as a security threat when users are able to access restricted content by using VPN to bypass firewall rules set within an organization’s network.
Types of VPN
VPN connections can be classified into three basic types:
- Remote user VPN
- Third-party VPN to mask source IP and user activities
- Site-to-site VPN
Remote user VPN
One common form of VPN enables a remote user, whether an employee, student or other authorized user, to access a private local network across the internet. Users establishing this type of connection require a VPN client in the form of software or an application such as the built-in Windows 10 VPN tool configured to connect to a VPN gateway on the local network.
Third-party VPN
This type of VPN also gives users the ability to remotely connect to other systems or networks, but with the intention to particularly mask their source and destination IPs by connecting to a third-party VPN provider, thus bypassing firewall rules. The use of third-party VPN is now on the increase due to the fact that most users want to hide their online activities from their employers.
Site-to-site VPN
This type of VPN is mostly established between routers or other endpoints located at different locations. In corporate setups, site-to-site VPNs may be established between branches for access to intranet systems.
Configuring VPN using Windows 10
Even though there are VPN clients such as OpenVPN, OpenConnect and CiscoAnyConnect, this article will focus on how to configure Remote User VPN using Windows 10.
VPN lab
In this lab, we will set up a point-to-point tunneling protocol VPN server on a Mikrotik router. The aim of this lab is to access the server located at 192.168.8.1. Note that this server is not reachable until VPN is successfully established.
Figure 1: Configuring Mikrotik router — PPTP server setup
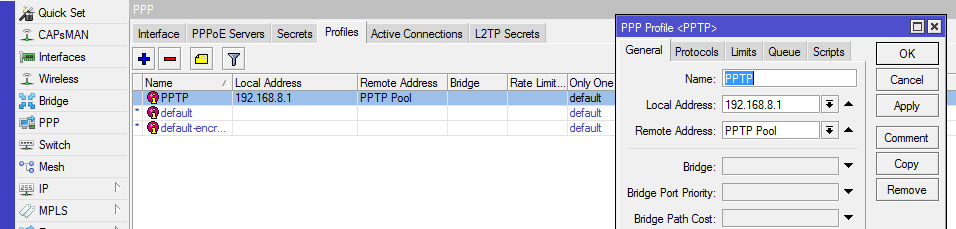
Figure 2: Configuring Mikrotik router — PPTP profile setup
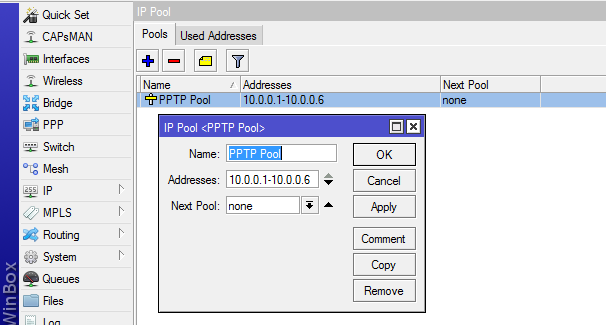
Figure 3: Configuring Mikrotik router — defining PPTP pool
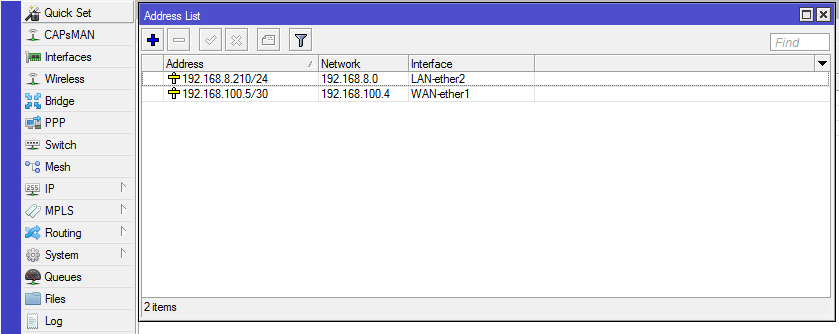
Figure 4: Configuring Mikrotik router — PPTP WAN and LAN interfaces setup
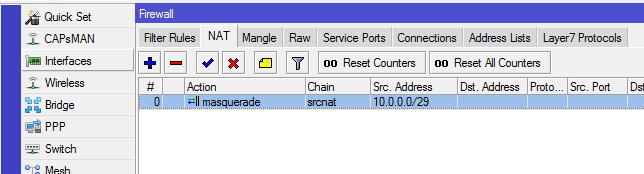
Figure 5: Configuring Mikrotik router — firewall and NAT setup
Windows 10 VPN setup
Once the VPN server has been set up on the Mikrotik server, the next action is to create a user profile which will connect to the server. The steps below illustrate how VPN is configured on a Windows 10 platform.
To start setting up a user profile for VPN, lets launch control panel and select Network and Sharing Center.
Select Change Adaptor Settings and then set a static IP address and then save settings.
Verify the WAN IP configuration by running the command ipconfig from the command prompt.
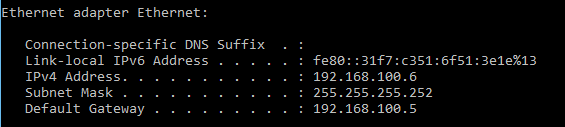
Figure 6: Verifying static IP configuration for the WAN connection to the Mikrotik router
Navigate to Settings and select Network & Internet. From the left pane, select VPN and then Add a VPN connection.
Complete the settings required and save those settings.
Select the VPN name PPTP and connect.
The status of the VPN connection should now change to connected if all parameters are correct.
After successfully creating a connection to the VPN server on the Mikrotik router, the Windows 10 endpoint will now be assigned an IP from the PPTP pool.
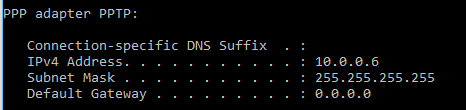
Figure 7: Verifying assigned VPN IP from command prompt
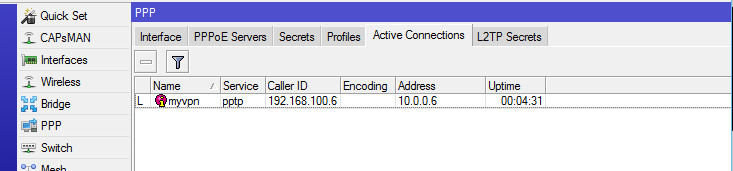
Figure 8: Verifying connectivity — active VPN connections on Mikrotik router
Access to the local server 192.168.8.1 is now possible after the VPN session is established.
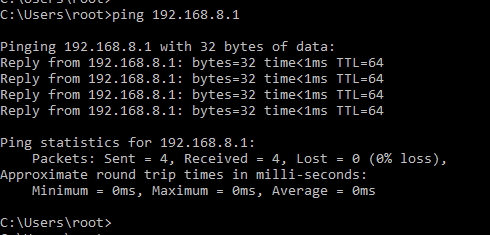
Figure 9: Verifying VPN connectivity — running a ping test to the local server
Learn Windows 10 Host Security
Conclusion
This article has defined the three basic connection types of VPN and illustrated how to configure a VPN server on a Mikrotik router. We also provided a guide on how to set up a VPN session using the built-in Windows 10 tool.
VPN access is now a necessity given to most users by their employers to allow them access to corporate systems and services while away from the office. The increased use of VPN to bypass firewall settings is now calling for a reassessment of corporate security settings.
Sources
- How Virtual Private Networks Work, Cisco
- IT Explained: VPN, Paessler







