SigintOS: Signal Intelligence via a single graphical interface [updated 2025]
SigintOS is a Linux distribution based on the Ubuntu Linux Operating System. This Linux distribution is built for signal intelligence and comes bundled with tools that use the preinstalled SigintOS software to make signal intelligence gathering possible. Through SigintOS, many SIGINT tasks can be done via a single graphical interface. These tasks include FM transmission, GPS transmission, GSM searching, IMSI catching, radio frequency jamming etc. You can download SigintOS version 1.1 here.

FREE role-guided training plans
Hardware requirements of SigintOS
To use SigintOS, you require a fairly powerful computer with reasonably acceptable specs. You also must have one of the following Software Defined Radios:
BladeRF: this is a software-defined radio platform that can be used to enable the exploration of radio frequencies. BladeRF gives you total control over the microcontroller, allowing you to reprogram the BladeRF as desired. You can acquire BladeRF from the BladeRF website in the sources section below.
HackRF: this is a software-defined radio that can allow you to transmit and receive radio signals between 1MHz and 6GHz. It can be used as a USB peripheral, allowing you to reprogram it for modern and next-generation radio technologies. You can acquire HackRFOne from the HackRFOne website in the sources section below.
RTL-SDR: this is a series of software-defined radios that are pocket-friendly. You can acquire RTL-SDR from the RTL-SDR website in the sources section below.
All of the above dongles are open source, relatively cheap and accessible to anyone and are a must-have to make any use of SigintOS.
Installation of SigintOS
You can install SigontOS on VMware Workstation. I managed to boot the ISO for installation and was presented with the screen below. On this screen, you can see the version of SigintOS as 1.1. You can also see an option to boot live in safe graphics mode, start the installer immediately, run a memtest and boot to the first hard disk.
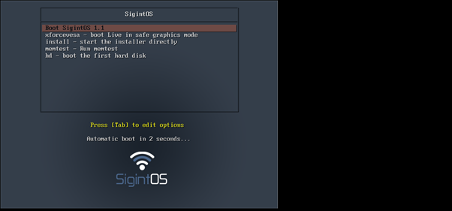
I boot live using the first option, "Boot SigintOS 1.1" and the loading screen below was presented.

Once SigintOS was fully loaded, I was presented with an Ubuntu user interface. This is because it is based on an Ubuntu 16.04 LTS distribution. The details of this particular live instance are shown below.
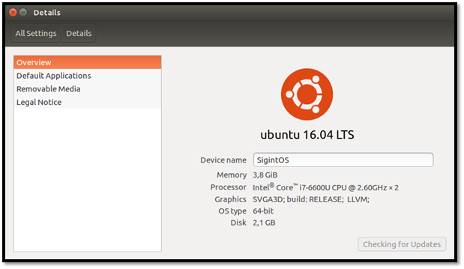
Features of SigintOS
I wanted to show you how you can launch the SigintOS tool. I did this by clicking on the first menu option within the Ubuntu interface. I then typed in "sigintos" and presented the two results as shown below.
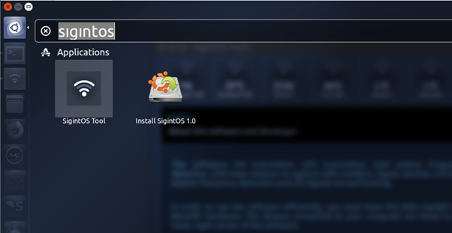
Clicking on the first option, "SigintOS Tool," I was presented with the SigintOS GUI. Within the GUI, I had seven options to choose:
FM transmitter, GPS transmitter, GSM search, IMSI catcher, LTE search and decoder and finally the jammer.
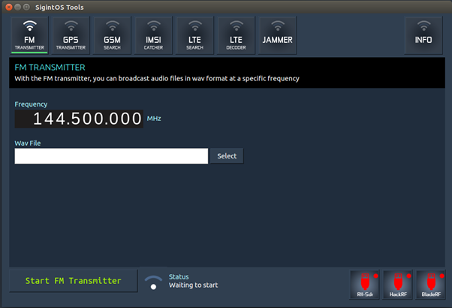
a) FM transmitter
The FM transmitter allows you to broadcast audio files in wav format at a frequency of your choice. You would need to select the wav file from the file system, then set the frequency in MHz. Once you have done that, ensure that you have selected either your RH-Sdr, HackRF or BladeRF, then click on "Start FM Transmitter."

What should you learn next?
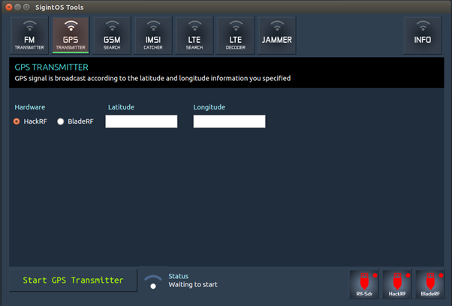
b) GPS transmitter
The GPS transmitter allows you to broadcast GPS information according to your specific GPS information. You would also need to specify the hardware to use. This option works with HackRF and BladeRF. Once you have input the longitude and latitude, you need to click on "Start GPS Transmitter."
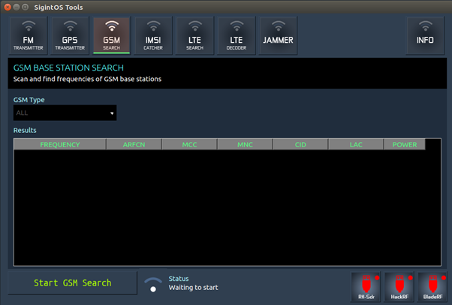
c) GSM search
The GSM search option allows you to scan and find frequencies of GSM base stations. You need to specify the GSM type, then click on "Start GSM Search." The results will be displayed on the GUI, with the frequency, ARFCN, MCC, MNC, CID, LAC and the GSM base station power.
This option is very important in discovering rogue GSM base stations, especially during a wireless penetration testing exercise.
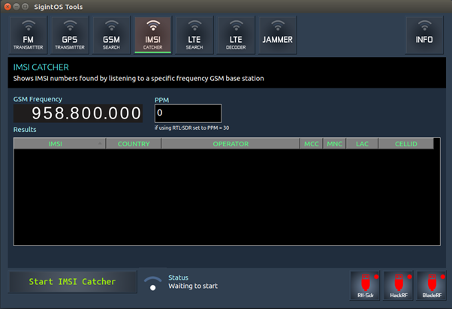
d) IMSI catcher
The IMSI catcher allows you to sniff IMSI numbers discoverable from a specified GSM base station. You would need to specify the GSM frequency and PPM. Once you have done that, you must click on "Start IMSI Catcher." This will begin the sniffing, and the results will be displayed on the GUI. The results will include various IMSI, countries, operators, MCC, LAC and cell id of all captured IMSI numbers.
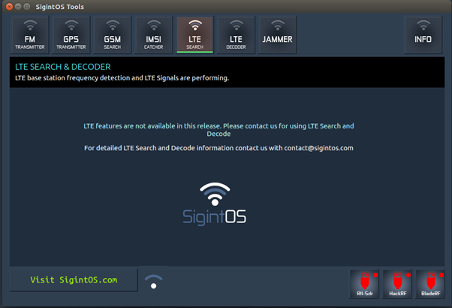
e) LTE search and LTE decoder
The LTE search allows you to detect LTE base station frequency detection. The LTE decoder option allows you to decode LTE frequencies. These options are not enabled within this latest release and will be enabled in future updates.
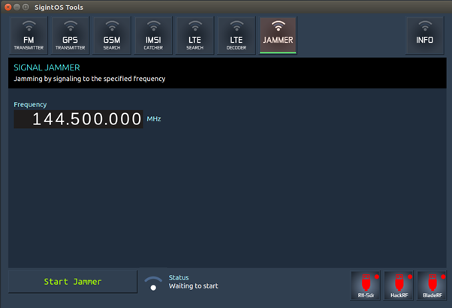
f) Jammer
The jammer allows you to jam the specified frequency in MHz. Once you have specified the frequency, click on the "Start Jammer" button. This will begin to jam the specified frequency.
Using SigintOS for signal intelligence gathering
SigintOS is the go-to operating system for signal intelligence gathering. With this operating system, you can perform several activities related to signal intelligence, which can be useful during a penetration test or if you would like to further understand how radio frequencies work.
Become a Certified Ethical Hacker, guaranteed!
Get training from anywhere to earn your Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Certification — backed with an Exam Pass Guarantee.
SigintOS also offers great support for software-defined radios, something that other penetration testing distributions such as Kali Linux do not offer since their purpose is not radio frequency hacking. It is also important for you to bear in mind that this operating system offers various other tools that you can use to understand more about radio frequencies, such as SDRangel and GNU Radio. However, I did not cover these tools since the main purpose of this article was the SigintOS single graphical interface called "SigintOS Tools."
Sources:
- SigintOS – Signal Intelligence Linux Distribution, cybarrior
- SNOOPING NETWORK TRAFFIC FROM LAN CABLES WITH AN RTL-SDR OR HACKRF, rtl-sdr.com
- SigintOS: A Wireless Pentest Distro Review, Tomas C. (Medium)
- GREAT SCOTT GADGETS, greatscottgadgets
- BladeRF, BladeRF








