Logical instructions in x86
This article defines logical instructions as executed by x86 processors. It goes on to describe four key classifications of logical instructions in brief.
This article is designed for students and professionals who want to gain a detailed understanding of logical instructions, their classifications and how they’re used. Through the use of an 8086 emulator, this article will give you a better understanding of logical instructions, its syntax and in some cases, memory flow during execution.
Intro to x86 Disassembly
Logical instructions in x86
The logical instructions define the set of operations performed by the processor Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). This article will discuss only the four key operations of logical instructions: AND, OR, XOR and NOT.
Basic format of instructions
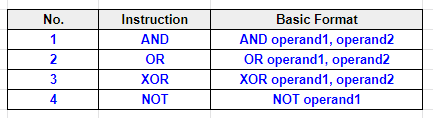
Table 1: Logical Instructions and their basic formats
The first operand in most cases refers to a register or memory. The second operand could be either in a register, memory or a constant value.
AND instruction
The AND instruction is used for performing operations on bits.
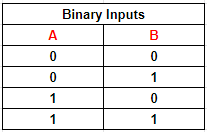
Table 2: Possible binary states for two inputs
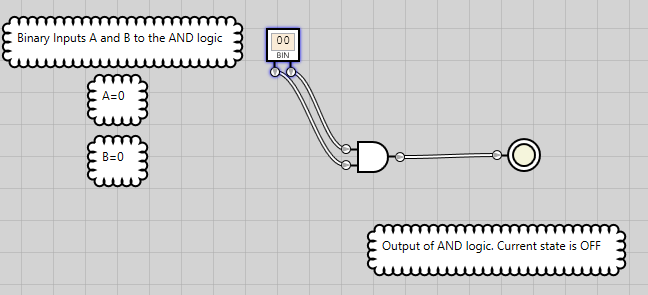
Figure 1: AND logic has an OFF state when both inputs are OFF
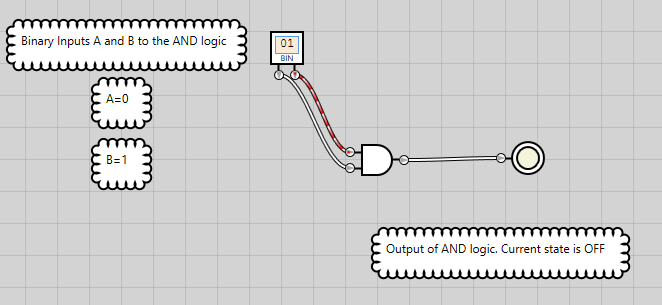
Figure 2: AND logic has an OFF state when either of the inputs are OFF
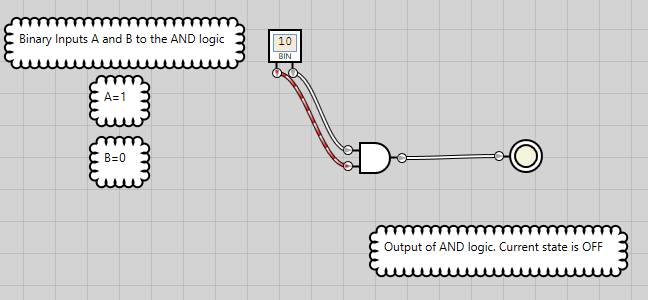
Figure 3: AND logic has an OFF state when either of the inputs is OFF
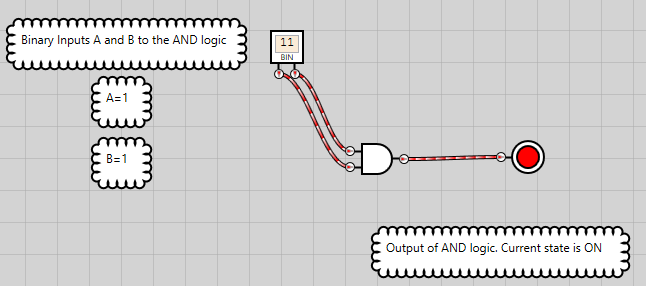
Figure 4: AND logic has an ON state only when both inputs are ON
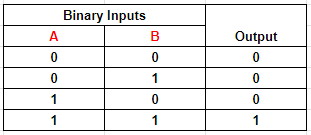
Table 3: Output of AND logic with two inputs
Following from figures 1 to 4, it can be summarized that the bitwise AND operation returns 1 if the matching bits from both inputs or operands are 1. Otherwise, it returns 0.
Example 1
- MOV AX, 10100011b ; Copy the binary value 10100011 to the accumulator
- MOV BX, 00111101b ; Copy the binary value 00111101 to register BX
- AND AX, BX ; Perform an AND operation on the values in registers AX and BX. Store the output in the accumulator
The AND operation is performed as shown below:
Operand1 (AX): 1010 0011
Operand2 (BX): 0011 1101
----------------------------------
Operand1(AX): 0010 0001
The accumulator AX will have the value 00100001 after the AND operation is executed. This value will be stored in the 8-bit low-order register AL of the accumulator.
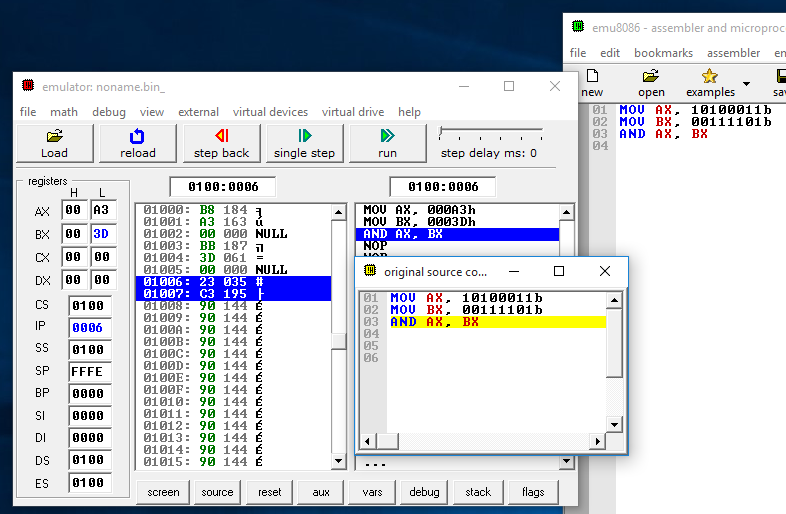
Figure 5: Contents of registers AX and BX before AND operation is executed
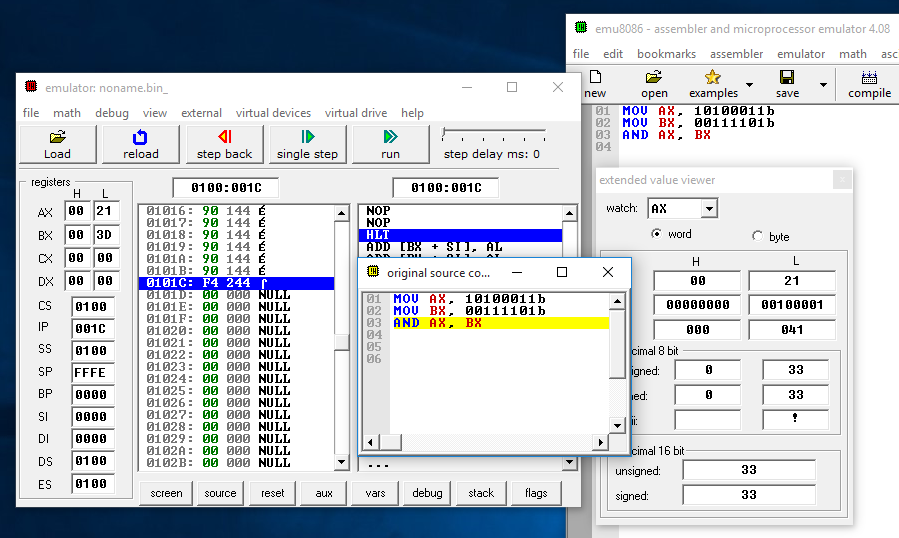
Figure 6: Contents of registers AX and BX after the AND operation is executed
OR instruction
The OR instruction is used for performing operations on bits. To understand how this works, we’ll run a logic gate simulator to generate the possible output states of OR logic for two binary inputs, A and B. These inputs are also the operands. Inputs to the OR logic are same as shown in Table 2.
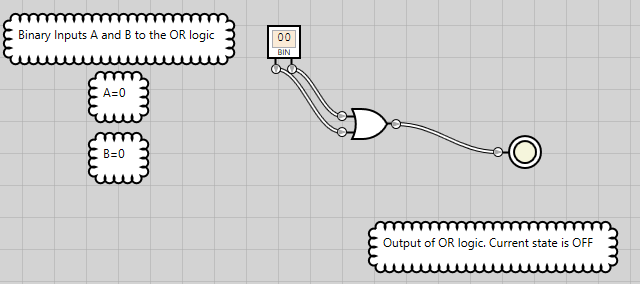
Figure 7: OR logic has an OFF state when both inputs are OFF
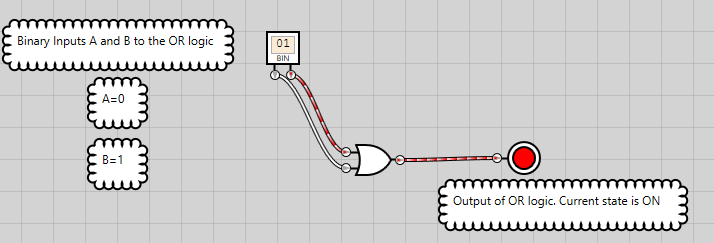
Figure 8: OR logic has an ON state when either of the inputs is ON
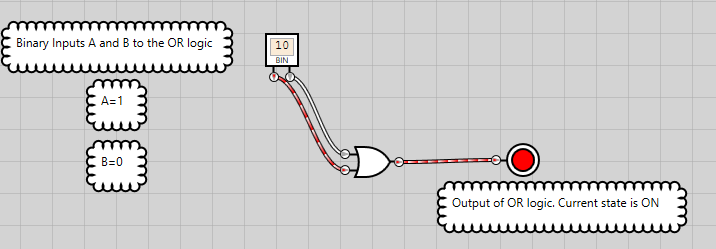
Figure 9: OR logic has an ON state when either of the inputs is ON
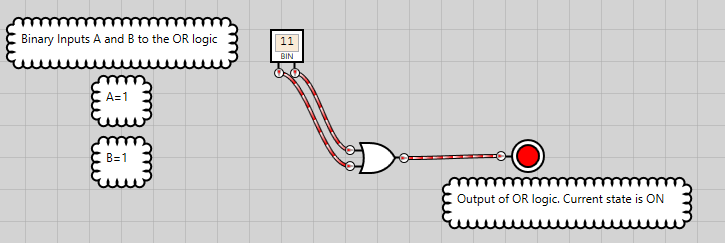
Figure 10. OR logic has an ON state when both inputs are ON
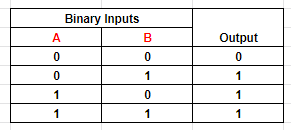
Table 4: Output of OR logic with two inputs
Following from figures 7 to 10, it can be summarized that the bitwise OR operation returns 1 if either of the bits at the input is 1. Otherwise, it returns 0. The output returns 1 when both inputs are 1.
Example 2
- MOV AX, 10100011b
- MOV BX, 00111101b
- OR AX, BX
The AND operation is performed as shown below:
Operand1 (AX): 1010 0011
Operand2 (BX): 0011 1101
----------------------------------
Operand1(AX): 1011 1111
The accumulator AX will have the value 10111111 after the OR operation is executed. This value will be stored in the 8-bit low order register AL of the accumulator.
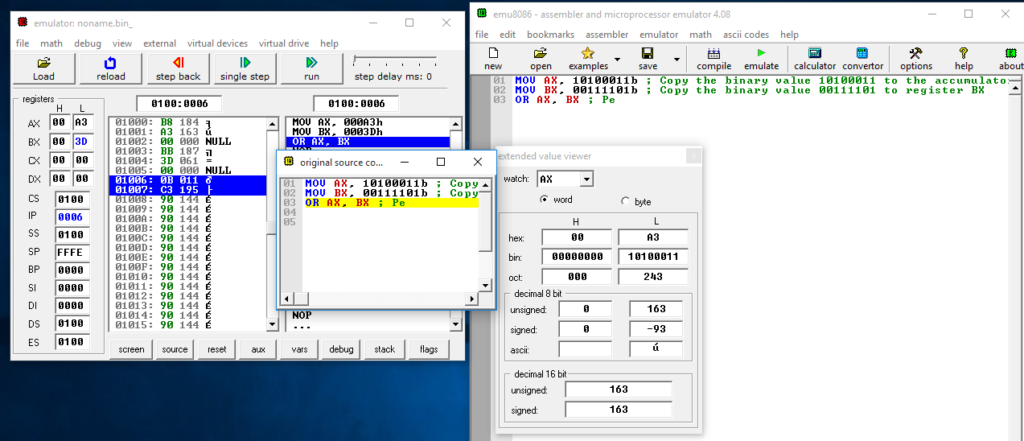
Figure 11: Contents of registers AX and BX before OR operation is executed
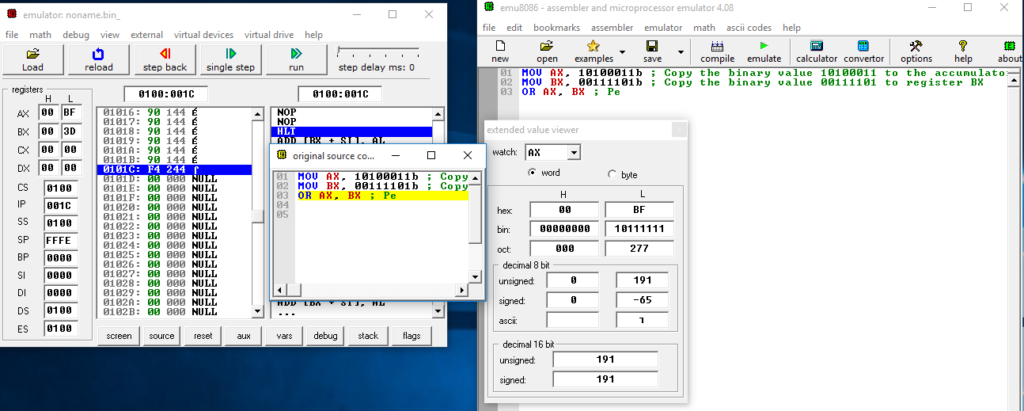
Figure 12: Contents of registers AX and BX after OR operation is executed
XOR instruction
The XOR instruction is used for performing operations on bits. We’ll make use of a simulator to generate the possible output states of XOR logic for two binary inputs A and B. These inputs also represent the instruction operands. Inputs to the XOR logic are the same as shown in Table 2.
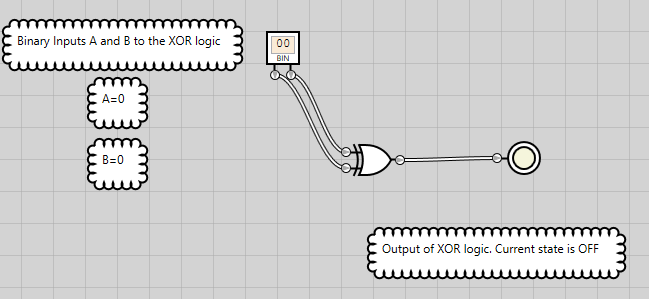
Figure 13: XOR logic has an OFF state when both inputs are OFF
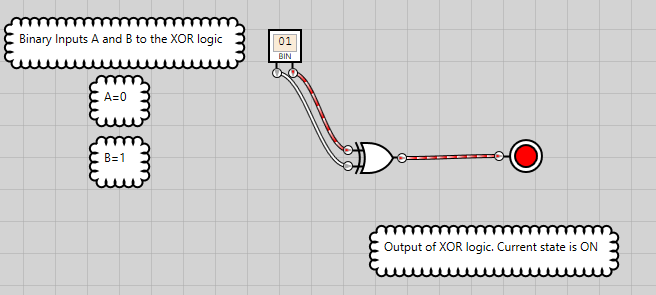
Figure 14: XOR logic has an ON state when either of the inputs is ON
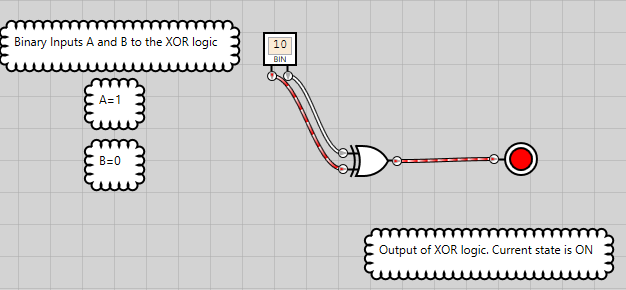
Figure 15: XOR logic has an ON state when either of the inputs is ON
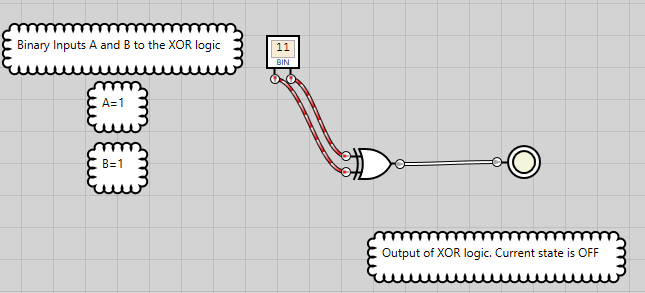
Figure 16: XOR logic has an OFF state when both inputs are ON
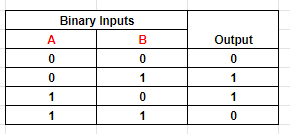
Table 5: Output of XOR logic with two inputs
Following from figures 13 to 16, it can be summarized that the bitwise XOR operation returns 1 only if either of the bits at the input is 1. Otherwise, it returns 0. The output returns 0 when both inputs are 1 or 0.
Example 3
- MOV AX, 10100011b
- MOV BX, 00111101b
- XOR AX, BX
The XOR operation is performed as shown below:
Operand1 (AX): 1010 0011
Operand2 (BX): 0011 1101
----------------------------------
Operand1(AX): 1001 1110
The accumulator AX will have the value 10011110 after XOR operation is executed. This value will be stored in the 8-bit low order register AL of the accumulator.
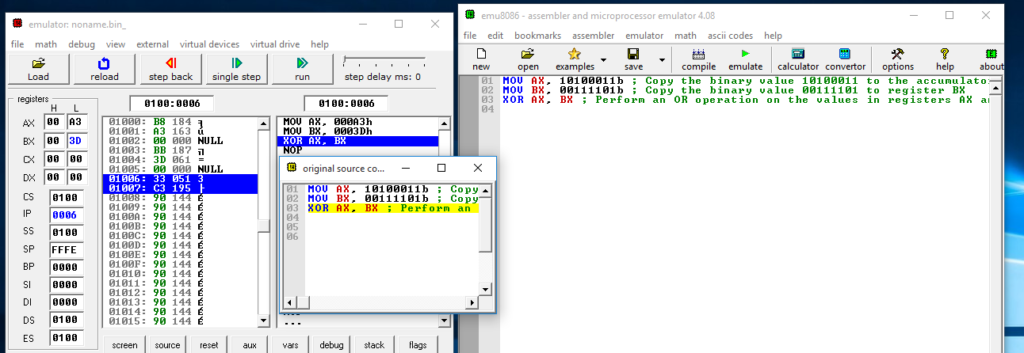
Figure 17: Contents of registers AX and BX before the XOR operation is executed
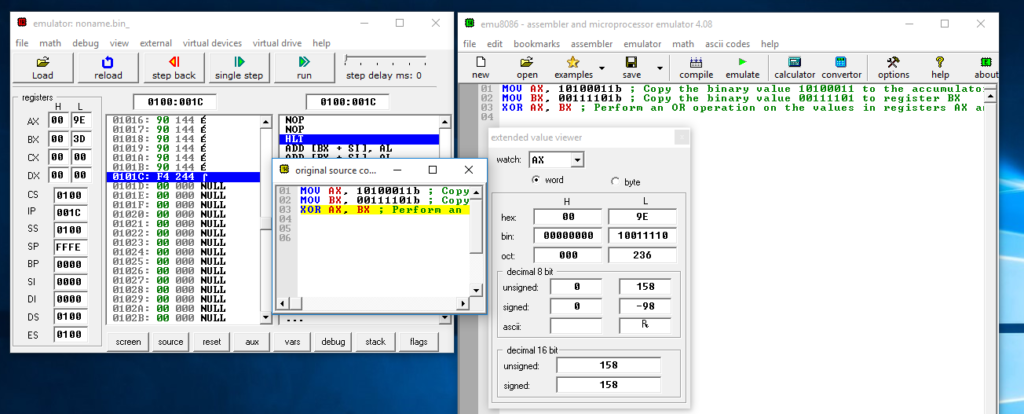
Figure 18: Contents of registers AX and BX after the XOR operation is executed
NOT instruction
The NOT instruction is used for performing operations on bits. This instruction reverses bits in an operand. Inputs to the NOT logic are shown below in Table 6.
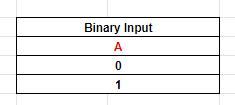
Table 6: Possible binary states for one input
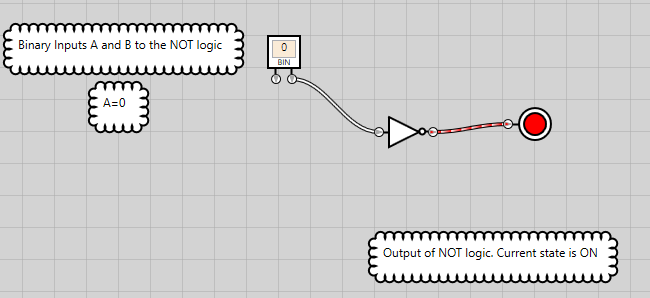
Figure 19: NOT logic has an ON state when the single bit input is OFF
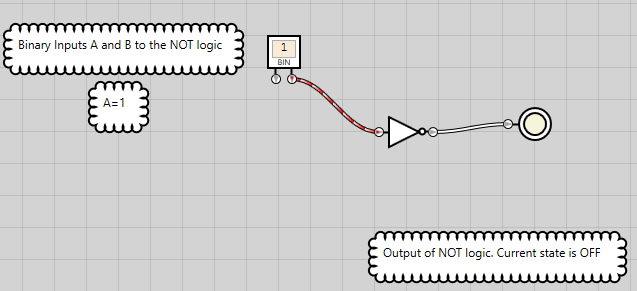
Figure 20: NOT logic has an OFF state when the single bit input is ON
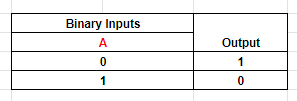
Table 7: Output of NOT logic with a single input
Example 4
- MOV AL, 10100011b
- NOT AL
The NOT operation is performed as shown below:
Operand1 (AL): 1010 0011
----------------------------------
Operand1(AL): 0101 1100
The accumulator AL will have the value 0101 1100 after the NOT operation is executed.
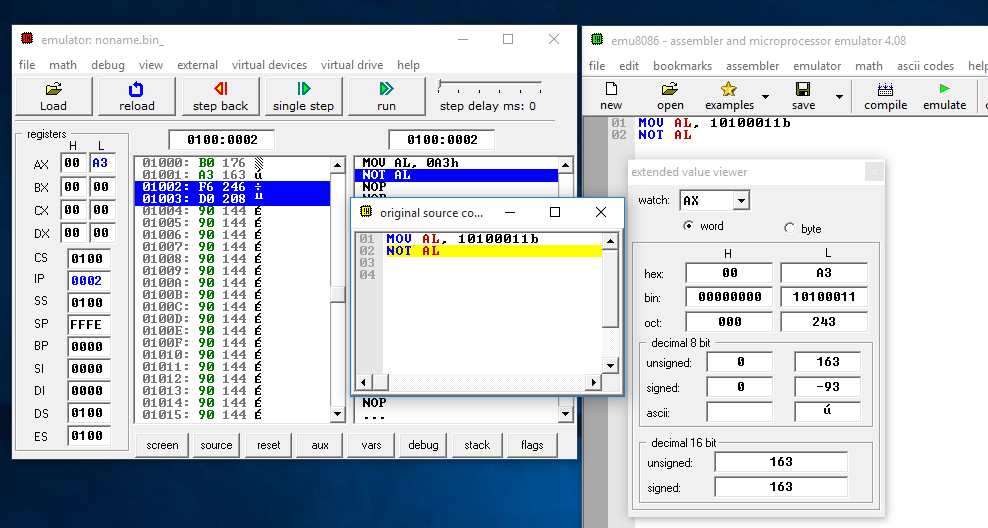
Figure 21: Contents of register AL before the NOT operation is executed
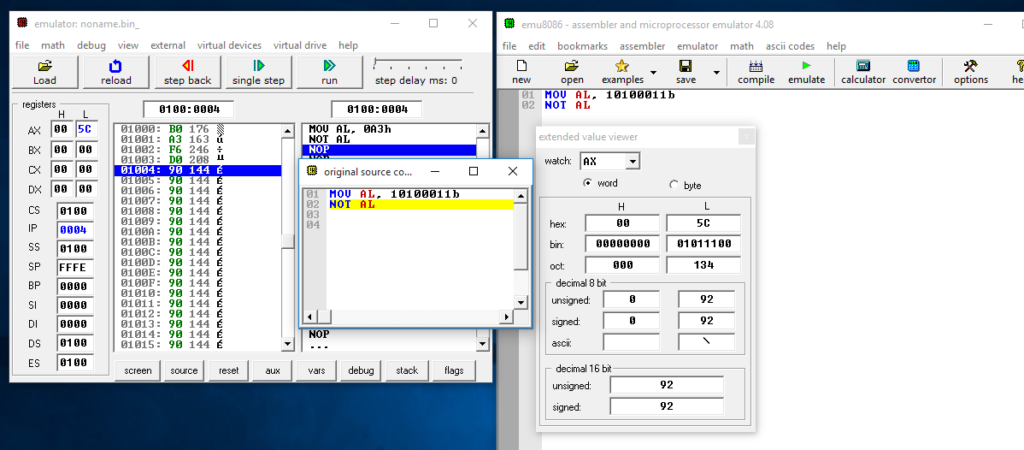
Figure 22: Contents of register AL after the NOT operation is executed
Conclusion
This article has explained four key instructions in logical operations. To adequately aid in the understanding of how the AND, OR, XOR and NOT operations work, the article has also presented the flow of instructions during their executions. These flows show contents of registers, particularly before and after operations are executed.
With all the four logical operations, the output of the analysis shown in the examples match the output and the content of registers after the operations are executed.
Intro to x86 Disassembly
Sources
Arithmetic Instruction, ScienceDirect






