Vault 7 Leaks: Inside the CIA's Secret Kingdom (July-August 07)
Introduction
Let's continue to analyze the information contained in files leaked by the organization Wikileaks and allegedly originating from a network of the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA).
The article includes key findings of documents leaked in July and August 2016
Hands-on threat intel training
At the time, we analyzed the following CIA projects since March:
- Project Protego – 07 September 2017
- AngelFire – 31 August 2017
- ExpressLane – 24 August 2017
- Couchpotato – 10 August 2017
- Dumbo– 03 August 2017
- Imperial – 27 July 2017
- UCL/RAYTHEON – 19 July 2017
- HighRise – 13 July 2017
- BothanSpy and Gyrfalcon – 06 July 2017
- OutlawCountry – 30 June 2017
- ELSA malware – 28 June 2017
- Cherry Blossom – 15 June 2017
- Pandemic – 1 June 2017
- Athena – 19 May 2017
- AfterMidnight – 12 May 2017
- Archimedes – 5 May 2017
- Scribbles – 28 April 2017
- Weeping Angel – 21 April 2017
- Hive – 14 April 2017
- Grasshopper – 7 April 2017
- Marble Framework – 31 March 2017
- Dark Matter – 23 March 2017
13 July 2017 - CIA HighRise Android malware
In July, WikiLeaks released a batch of documents included in the Vault 7 leak related to another CIA hacking tool dubbed HighRise.
HighRise is an Android application used by the US cyberspies to intercept and redirect SMS messages to a server controlled by the CIA.
Below the list of features implemented by the Android malware:
- Proxy "incoming" SMS messages received by HighRise host to an internet LP
- Send "outgoing" SMS messages via the HighRise host
- Provide a communications channel between the HighRise field operator & the LP
- TLS/SSL secured internet communications
"HighRise is an Android application designed for mobile devices running Android 4.0 to 4.3. HighRise provides a redirector function for SMS messaging. There are a number of IOC tools that use SMS messages for communication and HighRise is an SMS proxy that provides greater separation between devices in the field ("targets") and the listening post." reads the manual.
According to a user manual leaked by Wikileaks, the malicious code only works on Android versions from 4.0 through 4.3 (Android Ice Cream Sandwich and Jelly Bean) that currently account for 8,8 percent of overall Android devices on the market.
It is important to note that the leaked document is dated back to December 2013, it is likely that the CIA has updated the tool to target also newer versions of the Android OS.
The HighRise tool is packaged inside an app named TideCheck (tide check-2.0.apk, MD5: 05ed39b0f1e578986b1169537f0a66fe).

Figure 1 - Highrise malware
The tools could not be used to compromise Android devices remotely. Instead, it needs to be manually installed by CIA agents on the target system and needs to be manually executed at least one time.
"Therefore, the HighRise application first must be manually run once before it will automatically run in the background or after a reboot. As a consequence, the HighRise application now shows up in the list of installed apps so the HighRise operator can start it." continues the manual.
When running the tool for the first time, CIA cyber spies must activate it by entering the special code "inshallah" ("God willing" in Arabic) to access its settings.
Once the tool has been activated, it runs in the background listening for events, and it will automatically start every time the phone is powered on.
"Once activated, HighRise will run in the background listening for events. It will also automatically start when the phone is powered on. Activating HighRise multiple times will have no adverse effects." continues the manual.
19 July 2017 - UCL/RAYTHEON
In July Wikileaks published documents from Vault 7 leaks that revealed details about the prolific collaboration between the US Intelligence agency and tech firms Raytheon for malware development.
The documents show that the CIA contractor Raytheon Blackbird Technologies was tasked to analyze advanced malware and TTPs used by threat actors in the wild as part of the UMBRAGE project.
The Umbrage team is a CIA special unit tasked with false flag hacking operations.
According to the documents leaked by WikiLeaks, Raytheon Blackbird Technologies produced at least five reports to CIA as part of UMBRAGE Component Library (UCL) project between November 2014 and September 2015.
"Today, July 19th, 2017, WikiLeaks publishes documents from the CIA contractor Raytheon Blackbird Technologies for the "UMBRAGE Component Library" (UCL) project. The documents were submitted to the CIA between November 21st, 2014 (just two weeks after Raytheon acquired Blackbird Technologies to build a Cyber Powerhouse) and September, 11th 2015. They mostly contain Proof-of-Concept ideas and assessments for malware attack vectors – partly based on public documents from security researchers and private enterprises in the computer security field." states Wikileaks.
"Raytheon Blackbird Technologies acted as a kind of "technology scout" for the Remote Development Branch (RDB) of the CIA by analyzing malware attacks in the wild and giving recommendations to the CIA development teams for further investigation and PoC development for their own malware projects."
The experts from the firm also provided proof-of-concept ideas and malware attack vectors to the Intelligence Agency. The reports were commissioned by the CIA to gather information for the CIA's Remote Development Branch (RDB) aimed to collect ideas for developing their own advanced malware.
Below the information contained in the reports provided by the Raytheon Blackbird Technologies.
Report 1 — Researchers at Raytheon detailed a variant of the HTTP Browser Remote Access Tool (RAT), used by EMISSARY PANDA. This new variant was built in March of 2015 and is deployed through an unknown initial attack vector.
The RAT was used in cyber espionage campaigns by the Chinese APT group called 'Emissary Panda.'
Report 2 — The report details a new variant of the NfLog Remote Access Tool (RAT), also known as IsSpace, used by the SAMURAI PANDA APT group. The variant analyzed in the report is deployed using a repurposed version of the leaked Hacking Team Adobe Flash Exploit which leverages CVE-2015-5122. This new variant also incorporates the use of the Google App Engine (GAE) hosting to proxy communications to its C2 Server.
Report 3 — This report is a high-level analysis of "Regin" espionage platform that was first detected in 2014. The Regin cyberespionage tool is believed to be developed by the NSA intelligence agency.
"This report is a fairly high-level overview of Regin, a very sophisticated malware sample that has been observed in operation since 2013. There are some indications that the malware has been in use since as early as 2008, but most agree that the current iteration of Regin dates to about 2013." states the report. "Regin appears to be focused on target surveillance and data collection. The most striking aspect of Regin is its modular architecture, which affords a high degree of flexibility and tailoring of attack capabilities to specific targets. Another impressive aspect of Regin is its stealthiness, its ability to hide itself from discovery and portions of the attack are memory resident only."
Report 4 — The report details the "HammerToss" malware which was discovered in early 2015. The HammerToss is believed to be malicious code developed by Russian State-sponsored hackers that were being operational since late 2014.
"HammerToss is an interesting piece of malware because of its architecture, which leverages Twitter accounts, GitHub or compromised websites, basic steganography, and Cloud-storage to orchestrate command and control (C2) functions of the attack." states the report.
Report 5 — This document details the self-code injection and API hooking methods of information-stealing Trojan called "Gamker."
"This report details the code injection and API hooking methods of an information-stealing Trojan known as Gamker. This August 2015 three-page report from Virus Bulletin contains more technical detail than many 30+ page reports from other sources. We recommend a continued review of Virus Bulletin reports going forward." states the report.
27 July 2017 - Imperial project
In July Wikileaks published another batch of classified documents from the CIA Vault 7 leak, it includes details of the Imperial project.
The CIA project codenamed 'Imperial' includes details of three CIA hacking tools and implants that have been designed by the US intelligence to hack into computers running Apple Mac OS X and different Linux distributions.
The three hacking tools are:
- Achilles — A tool to trojanize a legitimate OS X disk image (.dmg) installer.
- SeaPea — A Stealthy Rootkit for Mac OS X Systems
- Aeris — An Automated Implant for Linux Systems
Achilles
Achilles is a hacking tool that allows CIA operators to package malicious codes with a legitimate Mac OS app into a disk image installer (.DMG) file. According to the documents, Achilles v1.0 was developed in 2011; the CIA experts only tested it on Mac OS X 10.6 (Apple Snow Leopard OS launched in 2009).
The tool is a shell script written in Bash that gives the operators "one or more desired operator specified executables" for a one-time execution.
In a classic attack scenario, the target individuals download an infected disk image on their computer, once they will open and install the software, the malware would run in the background.
Once the malware is executed, it will erase any trace of the Achilles from the downloaded application so that the file would "exactly resemble" the original legitimate software. This behavior makes hard the investigation of the malware from security experts and antivirus software.
SeaPea
The SeaPea hacking tool is a Mac OS X Rootkit that gives CIA operators stealth and tool launching capabilities by hiding important files, processes, and socket connections from the users.
It was developed in 2011, according to the documents SeaPea works on computers running then-latest Mac OS X 10.6 (Snow Leopard) Operating System (32- or 64-bit Kernel Compatible) and Mac OS X 10.7 (Lion) Operating System.
CIA operators need a root access to infect the target Mac computer; the hacking tools can be removed reformatting the startup disk or upgrading the OS to the next version.
Aeris
The Aeris hacking tool is an automated implant written in C programming language that could be used to backdoor portable Linux-based Operating Systems, including Debian, CentOS, Red Hat, FreeBSD, and Solaris.
Below the list of features implemented by Aeris:
- Configurable beacon interval and jitterStandalone and Collide-based HTTPS LP support
- Standalone and Collide-based HTTPS LP supportSMTP protocol support
- SMTP protocol supportTLS Encrypted communications with mutual authentication
- TLS Encrypted communications with mutual authentication
- Compatibility with the NOD Cryptographic Specification
- Structured command and control that is similar to that used by several Windows implants
- Automated file exfiltration
- Simple and flexible deployment and installation
Aeris is a builder that CIA operators can use to generate custom implants, it does not have a separate installer and to be deployed operators just need to place an Aeris binary in the desired directory.
"Aeris does not have a separate installer. To deploy it, simply place an Aeris binary in the desired directory. Rename the binary in any way that you wish. Note that the configuration is patched in at build time; hence, no additional files (beyond possibly those related to persistence — see the next section) are needed." states the user guide.
03 August 2017 - Dumbo tool
In August, Wikileaks revealed the details of a tool codenamed 'Dumbo' that was developed designed to disable security cameras and corrupts recordings.
The tool can identify installed devices like webcams and microphones, either locally or connected by wireless (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi) or wired networks; the documents revealed that CIA agents have to execute "Dumbo" directly from a USB thumb drive in the targeted device.
Dumbo requires SYSTEM privileges to perform its activity; it supports 32bit Windows XP, Windows Vista, and newer versions of Windows operating system. 64bit Windows XP or Windows versions before XP are not supported.
The tool can mute microphones, disable network adapters, and suspend processes utilizing webcams and corrupt any video recordings.
"Dumbo is a capability to suspend processes utilizing webcams and corrupt any video recordings that could compromise a PAG deployment. The PAG (Physical Access Group) is a special branch within the CCI (Center for Cyber Intelligence); its task is to gain and exploit physical access to target computers in CIA field operations." states the description of the tool provided by Wikileaks.
Dumbo also reports operators where footage files are stored allowing their corruption or deletion.
"[The tool] identifies installed devices like webcams and microphones, either locally or connected by wireless (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi) or wired networks. All processes related to the detected devices (usually recording, monitoring or detection of video/audio/network streams) are also identified and can be stopped by the operator," WikiLeaks said. "By deleting or manipulating recordings, the operator is aided in creating fake or destroying actual evidence of the intrusion operation."
According to the user guide leaked by Wikileaks, the cyberspies are aware that Personal Security Products such as the Kaspersky antivirus may block the installation of the device driver necessary to perform Dumbo operations.
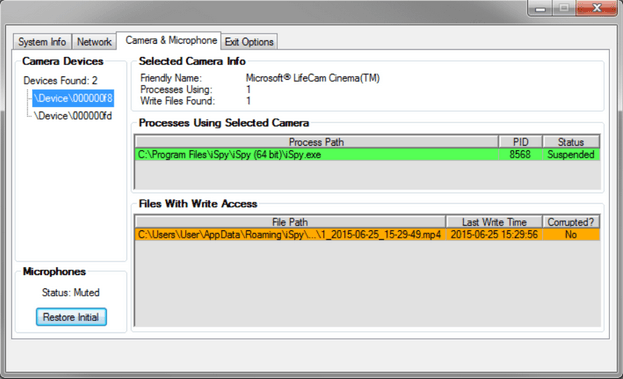
Figure 2 - Dumbo Tool
10 August 2017 – CIA CouchPotato
On August WikiLeaks published detailed documents of the CIA tool CouchPotato that allows operators to spy on video streams in real-time remotely.
The documents explain how the tool could be used by cyber spies to capture RTSP/H remotely.264 video streams. The Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP), is a network control protocol designed for controlling streaming media servers.
"Today, August 10th, 2017, WikiLeaks publishes the User Guide for the CoachPotato project of the CIA. CouchPotato is a remote tool for collection against RTSP/H.264 video streams. It provides the ability to collect either the stream as a video file (AVI) or capture still images (JPG) of frames from the stream that is of significant change from a previously captured frame. It utilizes FFmpeg for video and image encoding and decoding as well as RTSP connectivity. CouchPotato relies on being launched in an ICE v3 Fire and Collect compatible loader." states Wikipedia.
The CouchPotato tool utilizes FFmpeg for video and image encoding and decoding and Real Time Streaming Protocol connectivity. The CouchPotato tool is hard to detect, it supports the file-less ICE v3 "Fire and Collect" loader, which is an in-memory code execution (ICE) technique.
"CouchPotato is a remote tool for collection against RTSP/H.264 video streams. It provides the ability to collect either the stream as a video file (AVI) or capture still images (JPG) of frames from the stream that is of significant change from a previously captured frame. CouchPotato utilizes FFmpeg for video and image encoding and decoding as well as RTSP connectivity." reads the user guide. "to minimize the size of the DLL binary, many of the audio and video codecs along with other unnecessary features have been removed from the version of ffmpeg that CouchPotato is built with. pHash, an image hashing algorithm, has been incorporated into ffmpeg's image2 demuxer to provide image change detection capabilities. CouchPotato relies on being launched in an ICE v3 Fire and Collectcompatible loader."
The documentation leaked by Wikileaks does not provide details on how the CIA operators compromise the target systems, security experts speculate the CouchPotato tool needs to be used in conjunction with other hacking tools to break into the targeted systems.
24 August 2017 – ExpressLane
The ExpressLane tool was used by CIA to covertly collect data from liaison intel services, including FBI, DHS, and the NSA, to gather data from their systems.
On August, WikiLeaks published a batch of documents from Vault 7 leak that details how the CIA spies on other intelligence agencies, including FBI, DHS and the NSA, to gather data from their systems.
The CIA allows partner agencies to voluntary share biometric data using biometric collection system it provides.
The biometric software system provided by the CIA to its partners is based on a product from the US firm Cross Match, which is specialized in biometric software for law enforcement and the intelligence agencies.
The company made the headlines when its software was used to "identify Osama bin Laden during the assassination operation in Pakistan."
CIA exploited this system as a sort of backdoor in the partners' infrastructure; the tool code-named ExpressLane was developed by the CIA Office of Technical Services (OTS) to exfiltrate data collections from their systems secretly.
The CIA agents manually install the spying system as part of a routine upgrade to the Biometric system.
"The OTS (Office of Technical Services), a branch of the CIA, has a biometric collection system that is provided to liaison services around the world — with the expectation for sharing of the biometric takes collected on the systems. However, this 'voluntary sharing' obviously does not work or is considered insufficient by the CIA, because ExpressLane is a covert information collection tool that is used by the CIA to secretly exfiltrate data collections from such systems provided to liaison services." states Wikileaks.
The OTS officers, who maintain biometric collection systems installed at partner services, visit their premises, and secretly install the ExpressLane Trojan while displaying a fake "upgrade Installation screen with a progress bar that appears to be upgrading the biometric software."
" If the biometric system has already been given to Liaison, ExpressLane 3.1.1 will be installed as part of an upgrade to the biometric system by the OTS officers who maintain it. This new version of ExpressLane contains an Upgrade Installation screen with a progress bar that appears to be upgrading the biometric software for a period of time." states the user guide.
"This installation program, however, is not upgrading any of the biometric software. OTS requested this capability as part of their cover for action. The installation time for the upgrade can be pre-determined by an OTS officer before running the program in front of the liaison service. While the upgrade screen is running, ExpressLane kicks off a collection to a watermarked thumb drive. If the OTS officers have filed for the biometric software that needs to be updated, ExpressLane 3.1.1 will copy those files to specific
locations as well."
"ExpressLane 3.1.1 will overtly appear to be just another part of this system. It is called: MOBSLangSvc.exe and is stored in WindowsSystem32." leaked CIA documents read.
"Covertly it will collect the data files of interest from the liaison system and store them encrypted in the covert partition on a specially watermarked thumb drive when it is inserted into the system."
The ExpressLane tool is composed of two utilities:
- Create Partition — This utility allows agents to create a covert partition on the target system. The partition is used to store the collected information in a compressed and encrypted form.

Figure 3 - Create Partition
- Exit Ramp — This utility lets the CIA officers exfiltrate the collected data stored in the hidden partition using a thumb drive when they revisit.

Figure 4 - Exit Ramp
According to the documents, the latest version ExpressLane 3.1.1 by default removes itself after six months of the installation. The OTA officers can change the date for the automatic removal
31 August 2017 - AngelFire
At the end of August, Wikileaks published the details of a new batch of documents from Vault 7 leaks related to a new implant, dubbed AngelFire that was used by CIA agents to infect systems running Windows OS.
AngelFire allows cyberspies to gain control of the infected systems; it is a persistent backdoor that infects the partition Boot Sector. According to the user manual leaked by WikiLeaks, the AngelFire requires administrative privileges to compromise the target system.
"Today, August 31st, 2017, WikiLeaks publishes documents from the Angelfire project of the CIA. Angelfire is an implant comprised of five components: Solartime, Wolfcreek, Keystone (previously MagicWand), BadMFS, and the Windows Transitory File system." reads Wikileaks.
"Like previously published CIA projects (Grasshopper and AfterMidnight) in the Vault7 series, it is a persistent framework that can load and execute custom implants on target computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system (XP or Win7)."
Below are the details of the five components composing the AngelFire framework:
- Solartime — It is the component that modifies the partition boot sector to load and execute the Wolfcreek (kernel code) every time the system boots up.
- Wolfcreek — It a self-loading driver (kernel code that Solartime executes) that loads other drivers and user-mode applications
- Keystone — It is part of the Wolfcreek implant that leveraged DLL injection to execute the malicious user applications directly into system memory without dropping them into the file system. It is responsible for starting malicious user applications.
- BadMFS — It is a is a library used to create a covert file system at the end of the active partition (or in a file on disk in later versions). It is used as a repository for the drivers and implants that Wolfcreek will start. All files are both encrypted and obfuscated to avoid string or PE header scanning.
- Windows Transitory File system — It is a new method of installing AngelFire, which allows the CIA operator to create transitory files for specific actions including installation, adding files to AngelFire, removing files from AngelFire, etc.
According to the documents, the 32-bit version of the CIA implant works against Windows XP and Windows 7, while the 64-bit implant can be used to infect Server 2008 R2, Windows 7.
To be continued … stay tuned!
References
https://wikileaks.org/vault7/document/HighRise-2_0-Users_Guide/HighRise-2_0-Users_Guide.pdf
https://wikileaks.org/ciav7p1/cms/page_2621751.html
https://wikileaks.org/vault7/#UCL / Raytheon
https://wikileaks.org/vault7/document/Aeris-UsersGuide/page-1/
https://wikileaks.org/vault7/#Imperial
https://wikileaks.org/vault7/#Dumbo
https://wikileaks.org/vault7/#CouchPotato
https://wikileaks.org/vault7/#ExpressLane
https://wikileaks.org/vault7/#Angelfire
http://securityaffairs.co/wordpress/60964/hacking/cia-highrise-android-malware.html
http://securityaffairs.co/wordpress/61168/intelligence/wikileaks-cia-raytheon-relationship.html
http://securityaffairs.co/wordpress/61430/hacking/wikileaks-vault-7-imperial.html
http://securityaffairs.co/wordpress/61648/hacking/wikileaks-cia-dumbo-tool.html
http://securityaffairs.co/wordpress/61894/hacking/couchpotato-cia-tool.html
http://securityaffairs.co/wordpress/62317/intelligence/expresslane-cia-hacking-tool.html
Hands-on threat intel training
http://securityaffairs.co/wordpress/62539/intelligence/cia-angelfire-implant.html









