How criminals leverage a Firefox fake extension to target Gmail accounts
Recently, malicious campaigns have been using fake web-browsers extensions commonly disseminated via Google Ads and other channels.
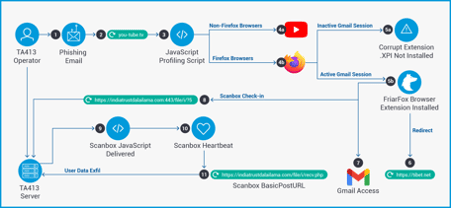
This article will Proofpoint researchers found a new Firefox fake extension active since March 2020 that targets Tibetan organizations globally. The fake extension, named FriarFox, is related to the TA413 gangue also observed delivering both Scanbox and Sepulcher malware campaigns against Tibetan organizations in early 2021.
Learn Vulnerability Management
How FriarFox spreads
The malicious campaign associated with the FriarFox fake extension impersonates the Tibetan Women’s Association using an email with the following subject: “Inside Tibet and from the Tibetan exile community.”
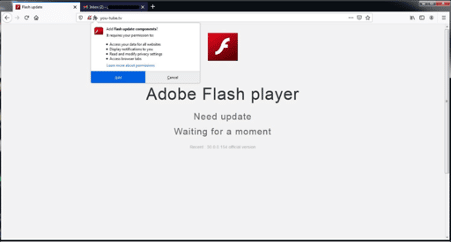
In detail, the email is sent from a known account that impersonates the Bureau of His Holiness the Dalai Lama in India and used by TA413 for several years. As observed in Figure 1, after clicking on an URL in the email body, a fake Adobe Flash installation screen is presented to convince the end-user to install the FriarFox Firefox extension.
Figure 1: High-level diagram of FriarFox fake extension.
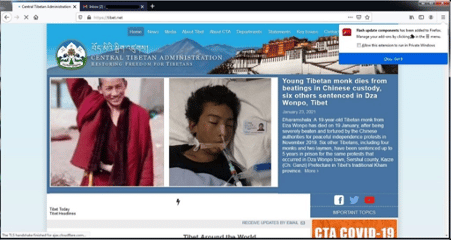
After accessing the fake Adobe Flash page, the user can add the extension as presented below. It’s also important to highlight that Adobe Flash is an EOF software, so internet end-users should be warned of this and about the critical consequences of installing extensions of this nature.
Figure 2: FriarFox extension installed on the victim’s web browser.
FriarFix data exfiltration
After a successful installation on the user’s side, the FriarFox browser extension can get details from Gmail accounts. In addition, the malicious extension contacts a C2 server to retrieve PHP and JavaScript-based payloads, including the Scanbox malware. The main features of the FriarFox extension are:
- Search emails
- Archive emails
- Receive Gmail notifications
- Read emails
- Alter Firefox browser audio and visual alert features for the FriarFox extension
- Label emails
- Marks emails as spam
- Delete messages
- Refresh inbox
- Forward emails
- Perform function searches
- Delete messages from Gmail trash
- Send mail from the compromised account
Scanbox malware:
- Access user data for all websites
- Display notifications
- Read and modify privacy settings
- Access browser tabs
Diving into the details
The FriarFox extension seems based on an open-source tool named “Gmail Notifier (restartless).” The legitimate extension allows users to receive notifications and perform specific Gmail actions on up to five Gmail accounts actively logged in simultaneously.
To carry out the malicious campaign, TA413 gangue changed several sections of the open-source extension Gmail Notifier to enhance its malicious functionality, conceal browser alerts to victims and disguise the extension as an Adobe Flash-related tool. In detail, the most notable changes were:
- The PNG icon appears as an Adobe Flash icon in the browser extension menu
- The extension metadata description supports refers a Flash update providing the description displayed in the browser extension menu
- All audio and visual browser alerts are set not to alert active users after the time of installation.
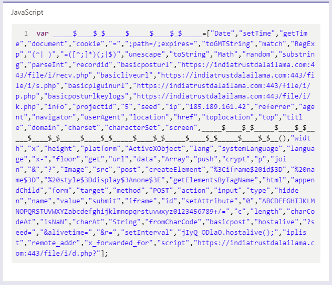
The fake extension communicates with the Scanbox JavaScript malware in later stages and implements its features. As observed below, the malware source code is obfuscated to make hard its detection and analysis.
Figure 3: Scanbox JS malware obfuscation layer.
After deobfuscating the malware, the configuration file can be observed, with the C2 server hardcoded and other configuration data.
Figure 4: Scanbox configuration deobfuscated.
By using this JavaScript malware, FriarFox turns itself into a potent Firefox Extension, able to access the browser opened tabs, data of all websites, display notifications, read and modify settings and more.
Learn Vulnerability Management
Final Thoughts
FriarFox is a complete browser extension capable of exfiltrating data from end-users Gmail Accounts and performing total control of the victim’s web browser. The usage of browser extensions to target the private Gmail accounts of users combined with the delivery of Scanbox malware demonstrates the malleability of TA413 when targeting communities.
Although there is no perfect formulate to fight attacks of this nature, it’s possible to mitigate in part the initial installation of browsers fake extensions following the security best practices, namely:
- Protect yourself against phishing attacks, and don’t click on untrusted/unknown URLs
- Check the publisher of the browser extension every time
- Avoid attachments from unofficial sources
In addition, watch out for updates. Extensions by default automatically will update themselves, which is helpful for security. Keep an eye out for unusual behavior and start taking malware protection seriously!
Sources
- FriarFox analysis, Proofpoint