Kali Linux: Top 8 tools for wireless attacks
Offensive Security's Kali Linux is a Debian-based Linux distribution used for penetration testing and security auditing. It is the most widely used toolset by security professionals for computer/digital, forensics, reverse engineering, security research and penetration testing. It is completely free of charge and contains over 100 penetration testing tools covering information gathering, vulnerability assessments, database assessments, wireless attacks, stress testing, web applications and more.
Wi-Fi has become integral in how we connect to the internet these days, and we use it across various devices such as laptops, smartphones, televisions, and appliances such as thermostats, toasters, refrigerators and more. However, this increases the risks to users and organizations.
The importance of carrying out a wireless security assessment with one of these top eight tools available on Kali Linux is crucial to your organization.
Want some FREE hacking training? We made a one-hour hacking with AI course, which includes a free interactive lab environment.

What should you learn next?
Why carry out a wireless security assessment?
Most organizations today have implemented wireless networking; however, they do not perform a security assessment on the wireless network. Inadequate configuration and existing vulnerabilities of the wireless network (and its underlying infrastructure) can lead to your IT infrastructure and business being compromised. Some of the benefits of performing a wireless security environment include:
- Helps to provide an understanding of how the wireless network is configured and how it fits into the rest of your IT environment.
- Helps to identify all the access points and assesses the vulnerabilities and security risks it presents to your IT environment and the business at large.
- Evaluates the adequacy of the security controls already in place.
- Helps to identify any unauthorized access points or rogue devices in your network.
- Helps organizations to meet audit and compliance requirements.
- Helps key stakeholders to assess the current state of the Wi-Fi environment and make decisions on how to address the risks the vulnerabilities identified pose to the organization.
Top 8 tools on Kali Linux for wireless attacks
The tools have been categorized into the following for ease of use:
- Bluetooth devices
- Wireless devices
Wireless devices
1. Aircrack-ng
This is the most widely used wireless password cracking tool. Aircrack-ng is a wireless security framework with a suite of tools used to capture wireless traffic. It is used to crack and recover WEP/WPA/WPA2 keys. The suite of tools can be used to perform the following: monitoring (capturing of network traffic), attack (carry out de-authentication attacks and replay attacks), testing (testing of hardware wireless capabilities) and cracking (WEP, WPA and WPA2 pre-shared keys).
Some of its features include:
- Can be run on Windows, Linux, iOS and Android platforms.
- Can be used to capture 802.11a/b/g traffic.
- Can be used to set up a rogue access point (evil twin attack).
- Can be used to crack and recover the WEP pre-shared key using the PTW approach or FMS/KoreK method. (statistical attacks in combination with brute-forcing) making it faster than other WEP password cracking tools.
- Can be used with any network interface card (NIC) which supports raw monitoring mode.
- Can be used for WPA/WPA2 pre-shared keys cracking using dictionary-based attacks.
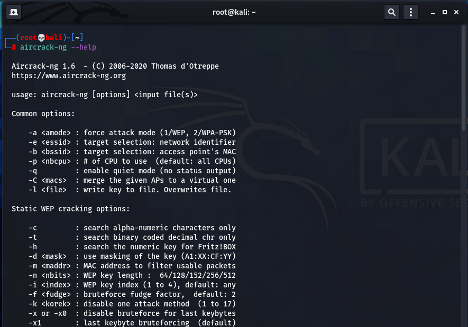
AirCrack-ng
2. Kismet
Kismet is an open-source wireless network device detector, sniffer, wardriving tool, GPS mapping tool and wireless intrusion detection system framework. It is a passive sniffer which allows it to discover hidden wireless networks while hiding itself. It works with Wi-Fi interfaces, Bluetooth interfaces and other specialized capture hardware. Some of its features include:
- Can be run on Windows, macOS and Linux platforms.
- Can be used to sniff 802.11a/b/g/n traffic.
- Can be used for its radio frequency monitoring mode (rfmon) which allows the user to monitor traffic and identify wireless networks without associating with an access point.
- Displays all the packets it captures without limiting it to those specific to one access point broadcasting under one SSID.
- Identifies WAPs in use, SSIDS and the type of encryption used on a network.
- Can be used to identify common trends in network usage, network strength and WAP configuration.
- Its logging standards are compatible with Tcpdump/WinDump and Wireshark.
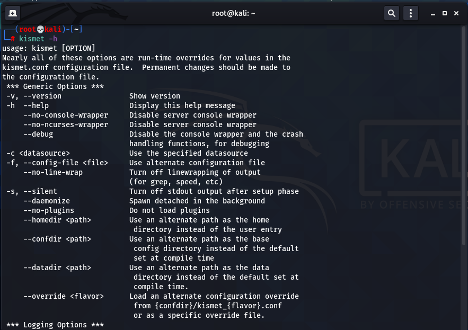
Kismet
3. Fern Wi-fi Cracker
This is a python-based tool with a graphical user interface used to perform wireless security audits and attacks. It is used to crack and recover WEP/WPA/WPS keys. It can also be used to carry out other network-based attacks on wireless and wired networks. Some of its features includes:
- Can be run on Windows, macOS and Linux platforms.
- Can be used for WEP cracking using attacks such as ARP Request Replay, Caffe-Latte attacks, Chop-Chop attacks and more.
- Can be used for WPA/WPA2 cracking using dictionary-based attacks or WPS-based attacks.
- Can be used to perform brute force attacks on HTTP, HTTPS, TELNET and FTP servers.
- Can be used for session hijacking in various modes such as passive modes, ethernet modes and more.
- Utilizes an automatic access point attack system.

Fern Wi-fi cracker
FREE role-guided training plans

4. Wifite
Wifite is used for attacking WEP/WPA/WPS encrypted wireless networks simultaneously. It can also be used for auditing wireless networks via a "set it and forget it" method. It utilizes the tools associated with Aircrack-ng, Reaver and PixieWPS. Some of its features include:
- Can be used to detect access points (targets) by their signal strengths and cracks the closest access points first.
- Can be easily customizable to automate the attack process (with settings around WEP/WPA/Both, above certain signal strengths, channels and more).
- Can be used to capture the required information needed for a pixie-dust attack by the PixieWPS tool.
- Makes the attacker anonymous by changing the attacker's MAC address before the attack and when the attack is completed.
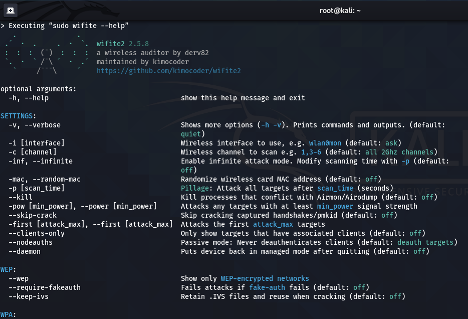
Wifite
5. PixieWPS
PixieWPS is a c-language-based tool used to brute-force the WPS pin offline (usually displayed at the back of a router). It uses the "pixie-dust attack" by exploiting a WPS vulnerability allowing the WPS pin to be recovered within seconds or minutes depending on the target (if vulnerable). Some of its features include:
- Checksum optimizations.
- Reduces the entropy of the seed from 32 bits to 25 bits for some access points.
- Before it can be used, it requires the following: enrollee public key, registrant public key, enrollee hash-1, enrollee hash-2, authentication session key and enrollee nonce. It is often run as part of Wifite.
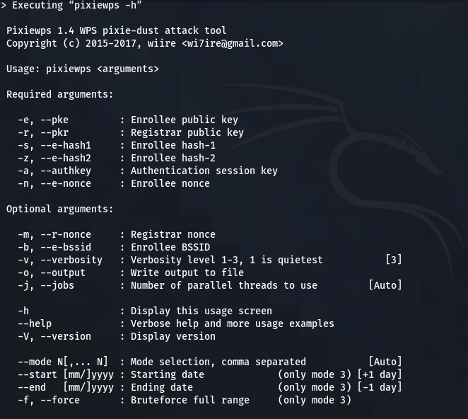
PixieWPS
6. WireShark
WireShark is a network sniffer and protocol analyzer used in intercepting and capturing network traffic and logging it for further analysis. These logs can be analyzed to detect data and information such as passwords sent in data packets across the network. Some of its features include:
- Can be run on Windows, Linux and iOS platforms.
- Provides a large number of built-in protocol dissectors allowing it to be able to identify different types of network traffic and breaks them into easily readable format.
- Provides built-in traffic coloring filtering and connection following to assist with log analysis.
- Can be run on promiscuous mode allowing Wireshark to capture all the packets it can over the network.
- Can be used to intercept and analyze encrypted TLS traffic.
- Can be used to listen to a real-time network connection.
Bluetooth devices
7. Spooftooph
Spooftooph is a tool used to automate spoofing or cloning of Bluetooth device information such as device name, class, address and more. Some of its features include:
- Can be used to clone and log Bluetooth device information
- Can be used to generate new Bluetooth profiles
- Can be used to change the Bluetooth profile every so many seconds
- Can be used to select devices to clone from a scan log
8. BlueMaho
BlueMaho is an open-source, python-based Bluetooth framework with a suite of tools used for testing the security of Bluetooth devices. Some of its features includes:
- Can be used to scan devices for information such as Service Discovery Protocol ("SDP") records, vendor information, device information and more.
- Can be used to track devices providing information about their location, the number of times the device has been seen and its name change history.
- Sends an alert when a new Bluetooth device has been identified.
- Can be used to configure actions to be carried when a new device has been identified.
- Allows the use of more than one Bluetooth adapter for testing (one can be used for scanning and the other used for running exploits).
- Can be used to test the device for known and unknown vulnerabilities.
- Can be used to change the name, class, mode and device address of local HCI devices.

FREE role-guided training plans
Being aware of the top Kali Linux tools for wireless attacks
In this article, we looked at some of the benefits of carrying out a wireless security assessment for organizations. We also provide an overview of specialized tools in Kali Linux which can be used in carrying out a wireless security assessment to identify wireless networks and Bluetooth devices, crack wireless network keys and identify vulnerabilities on network devices.
However, you have more options when it comes to protecting wireless networks. There are a range of other tools and methodologies you can explore. Suppose you want to dig deeper into network security. In that case, you can check out Infosec’s boot camps and courses that prepare you to earn valuable certifications and hone your cybersecurity skills. You can also check out our free course, Learn how to hack and use AI.








